Describe the Function of Schwann Cells
What are they and why are they necessary. The function of this sheath is to protect and direct the nerve impulses.
In Human Anatomy What Is The Purpose Of The Schwann Cells Socratic
Schwann cells are part of the peripheral nervous system PNS They have two major functions they produce the myelin sheath which covers the schwan cell which helps to repair and regenerate.

. By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework questions. They function a lot like oligodendrocytes in that they provide myelin sheaths for axons but they exist in the peripheral nervous system PNS rather than the CNS. The Schwann cells Also known as neurolemocitos constitute a specific type of glial cells of the nervous system of the brain.
Schwann cells are specific to the peripheral nervous system which consists of all of the nerve cells outside of the brain and spinal cord. These cells are equivalent to a type of neuroglia called oligodendrocytes which occur in the central nervous. Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS also include satellite cells olfactory ensheathing cells enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings such as the Pacinian corpuscleThe two types of Schwann cells are.
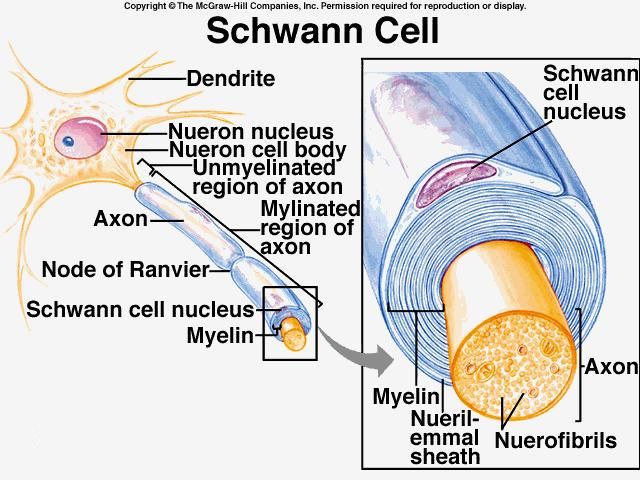
Schwann cells make up what is called the myelin sheath around the axon of the neuron. A dendrite b axon c cell body d myelin sheath e nodes of Ranvier f Schwann cells g motor neuron interneuron and sensory neuron 2. Schwann cells are named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann who discovered them in the 19th century.
Schwann cells serve as the myelinating cell of the PNS and support cells of peripheral neurons. If the axon reestablishes its normal synaptic contacts normal. These cells are located in the peripheral nervous system And its main function is to accompany the neurons during their growth and development.
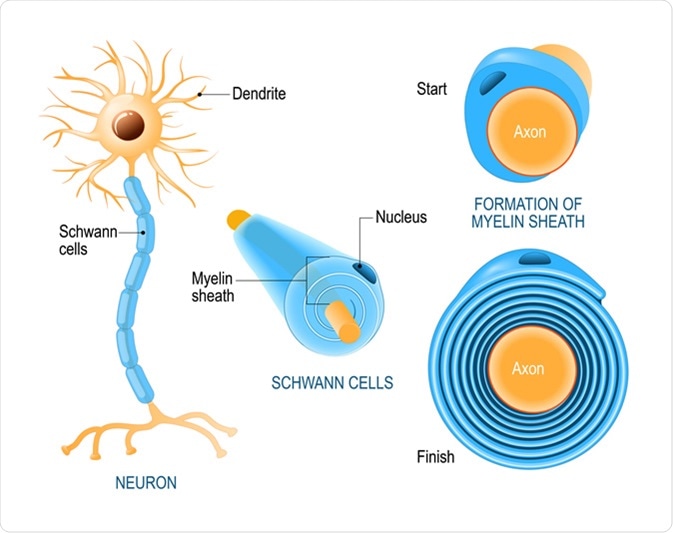
For the insulating myelin sheath to be produced by the Schwann cells the plasma membrane of these cells needs to wrap around the axons of the neuron. As the axon elongates the Schwann cells wrap around it. Schwann cells are named for physiologist Theodor Schwann who discovered them.
The cell body and nucleus of oligodendrocytes remain separate from the myelin sheath and so there. Describe the function of the. PNS Peripheral Nervous System are the major glial type in the PNS.
Schwann cells respond quickly to injury and aid axon regeneration. The conduction of nerve impulses across axons nerve growth and regeneration trophic support for neurons production of the nerve extracellular matrix regulation of neuromuscular synaptic function and. A schwann cell envelops and rotates.
Presentation of antigens to T-lymphocytes. Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells are types of glia the non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that carry out a wide variety of functionsSchwann cells are sometimes called neurilemma cells since the outer layer of the myelin sheath is also called the neurilemma. As the neuron recovers its axon grows into the site of injury and then distally along the path created by the newly divided Schwann cells.
Schwann cells produce the myelin sheath around the axon in peripheral nervous system. Schwann cells are characterized by covering the extensions of the Neurons. Schwann cells are associated with a number of demyelinating disorders infected during leprosy and are responsible for the tumors in both neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2.
The main function of Schwann cells is to support myelinated and unmyelinated nerve cell fibers. The myelin sheath provides electrical insulation. Develop from neural crest cells and differentiate by expressing transcription factor SOX-10.
Schwann cells myelinate axons of the peripheral nervous system PNS. A Schwann cell forms a myelin sheath by wrapping its plasma membrane concentrically around the inner axon. The regeneration failure in cJun cKO mice is due to the central function of cJun in Schwann cell reprogramming since this factor controls both components of the Schwann cell injury response dedifferentiation of myelin cells and activation of the repair programme ArthurFarraj et al.
Schwann cells are derived from neural crest cells and come in two types either myelinating or non-myelinating Schwann cells. Schwann cell functions provide a protective covering delivers material to and removes material from the neuron axon greatly increase the speed of impulse enable repair of PNS neurons. Both play a pivotal role in the maintenance and regeneration of axons of the neurons in the PNS.
Gap between adjacent Schwann cells. Describe the function of Schwann cells. However instead of being a central cell with membrane-tipped arms Schwann cells form spirals.
Schwann Cells Function. A Schwann Cell Schwann Cell Function. 604 Describe the structure and the function of Schwann cells which for myelin sheath.
The Schwann cell plays a vital role in maintaining the peripheral nervous system PNS. List some simple reflexes. If the Schwann cells are damaged it can cause a number of motor problems which can include paralysis.
Schwann cells take on many of the roles that nerve cells cannot complete themselves. Schwann cells have 4 basic roles when it comes to supporting nerves. While the nucleus remains fixed the inner turn of the glial cell membrane spirals around the axon to add membrane layers or.
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system PNS. Explain why babies are born with simple reflexes. To form the sheath Schwann cells wrap around a segment of an axon.
Schwann cell also called neurilemma cell any of the cells in the peripheral nervous system that produce the myelin sheath around neuronal axons. As they are separated by gaps of unsheathed axon in which impulses travel along the axon. If the myelin sheath that the Schwann cells make up becomes damaged then the impulses cannot flow properly very much like the function of a coating on an electrical wire.
Schwann cells are the principle glia which are neuron supports in the peripheral nervous system. Myelinating Schwann cells start forming myelin sheath as early as during the development of the foetus before birth. Schwann cells are a type of glial cells of the peripheral nervous system that help form the myelin sheath around the nerve fibers.
Myelin sheath of the neuron.

No comments for "Describe the Function of Schwann Cells"
Post a Comment